Conditional Actions
Conditional actions are used to make your form smart and are automatically applied to form elements when certain conditions are met.
The logical structure of these actions is of the IF/THEN type: IF (condition happens) THEN (do the action).
For example, you can use conditional actions to hide or show form elements when a certain condition happens, such as:
- IF option X of question Y is selected, THEN hide questions A, B, C and display questions D, E, F.
Conditional Actions are processed EVERYTIME a form response is changed. In other words, modifications made to a form will be applied to all previous responses.
To include conditional action
- Go to the desired element and click
or select the "Conditional actions" tab, at the top of the form editing screen;
- Click
;
- Choose the question that will determine the display condition;
- Choose the logical operator of the condition;
- Set the question answer to complete the display condition. Enter the expected answer or choose from answer options for the question chosen as the display condition;
- To include one more criterion in the presentation logic, click
;
- Set the attributes in Run when. See table below for more information;
- Click
to save the settings.
Conditional Action configuration features. Click on the image to enlarge it.
Conditional Action Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Conditions | Defines the logical conditions that must be met for the conditional action to be executed.
|
Display when | Defines which logical operator should be considered among the defined display conditions.
Example of logical operator Conjunction (AND)Consider the following conditional question: "Would you like to schedule an interview?" This question will only be displayed if all the following conditions are true:
In this scenario, the question about scheduling a meeting will only be displayed if the user demonstrated interest in the services, lives in Brazil, and has a specific income range. In other words, the logic would be: Only when all three conditions are met will the conditional question be displayed. If any of these conditions are not met, the question will be omitted from the form.
Example of logical operator Disjunction (OR)Consider the following conditional question: "Would you like to receive informational materials?" This question will be displayed if at least one of the following conditions is true:
In this scenario, the conditional question will be displayed if the user showed interest in the products, or is interested in receiving a "newsletter," or would like to receive promotions and offers: Thus, if any of these conditions are met, the question about receiving informational materials will be displayed.
|
| Apply actions to | Defines which elements the actions will be applied to. Choose between:
|
| Actions | Defines which action should be executed. Choose one of the available options or both:
When choosing the options above, it is possible to indicate which element(s) should be displayed or hidden in the form. |
| Elements to display | This field is shown when the "Display form elements" option is selected in the Actions field. Include the elements that should be displayed using the button The button |
| Elements to hide | This field is shown when the "Hide form elements" option is selected in the Actions field. Include the elements that should be hidden using the button The button |
Elements used in more than one conditional action
Notice in the following figure that the question 8 What makes you distrust brands that offer this type of product?
appear in more than one logical condition.
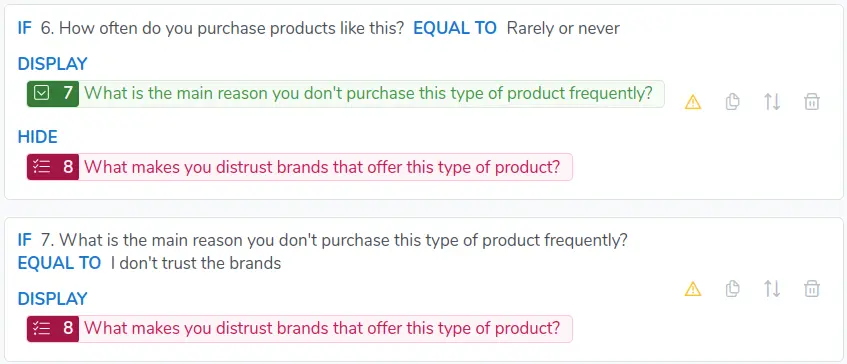
These logical conditions can be rewritten as follows:
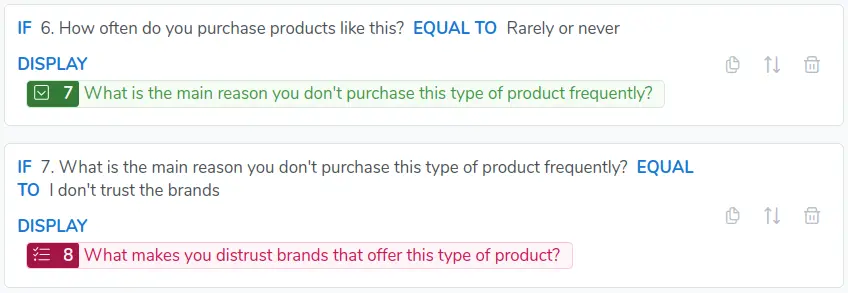
Note that the DISPLAY and HIDE actions are applied in a complementary manner, that is, when defining a condition to display a question, you are automatically defining the conditions under which such question will be hidden. So if the condition is met, the question will be displayed, if not, it will be hidden.
In the example, it is not necessary to create an Action to hide question 8, as it will be hidden automatically whenever
question 7 not equals to Rarely or never.