Integrations
What is system integration?
System integration is the process of connecting different systems or applications so that they can share information and work in a coordinated manner. Integration allows data and processes to flow between systems, eliminating information silos and improving operational efficiency, with the following objectives:
- Process automation: reduce manual and repetitive tasks, allowing systems to exchange information automatically;
- Information centralization: unify data from different sources, making analysis and decision-making easier;
- Productivity improvement: avoid rework and increase the speed of operational processes;
- User experience enhancement: provide an integrated and consistent view of data across different platforms.
How does system integration work in Hashdata?
System integration allows all data collections to be transferred directly from HashData servers to a local server (on-premises), a cloud server, or even third-party servers.
There are two integration options: via REST API or with Hashdata Advanced Reports.
- REST API
A REST API (Application Programming Interface Representational State Transfer) is a communication interface between systems that follows REST principles (Representational State Transfer), a network architecture style. Integration via REST API allows other systems to access data stored in Hashdata. Communication between systems occurs via HTTPS requests, using an authentication token to ensure information security.
- Hashdata Advanced Reports
Integration with Hashdata Advanced Reports enables the creation of advanced reports and dashboards updated in real time, meaning that the data entered in the forms is automatically exported to the reports and dashboards. Both dashboards and reports are easy to create and do not require specialized knowledge. Once configured, integrations and synchronizations are automatically performed by Hashdata in real time.
Enable integrations
To enable integrations, select the Integrations icon in the main menu (left sidebar). Then follow the page instructions and choose which integrations to enable.
Form Integration Configuration
After enabling integrations, it is necessary to define which forms should be integrated with Hashdata Advanced Reports and which should be exported via REST API.
- Select the form to enable the desired integration: Hashdata Advanced Reports, REST API, or both;
- Click
to configure the integrations;
- Define, for each element in the form, the question name, which is a short name that identifies the
element in the system. The question name is also used in mathematical formulas and data exports.
Use the button
, for the system to suggest the question name. Make adjustments if necessary;
- If integration with HashData Advanced Reports is enabled, the field Index name in Hashdata Advanced Reports will appear.
This field consists of a numeric value that should not be changed, followed by a description that must contain only
letters, numbers, underscores, and dashes, e.g.:
21261-form-personal-data;
Only forms marked for REST API export will be accessible via REST API. Likewise, only forms marked for integration with Hashdata Advanced Reports will be visible in the tool.
Form drafts can also be exported/integrated, but keep in mind that these forms can have their structure changed at any time.
Integration via REST API
Communication between systems is done via HTTPS requests, using an authentication token to guarantee information security. An authentication token is a unique alphanumeric sequence used to authenticate and authorize a user or application accessing a REST API. It works like a "digital key" that proves that whoever is making the request has permission to do so.
After enabling the REST API integration, you must select the forms accessible through this integration.
Access to data is done through end-points. The URIs for each resource are presented below, but first it is necessary to understand how authentication works.
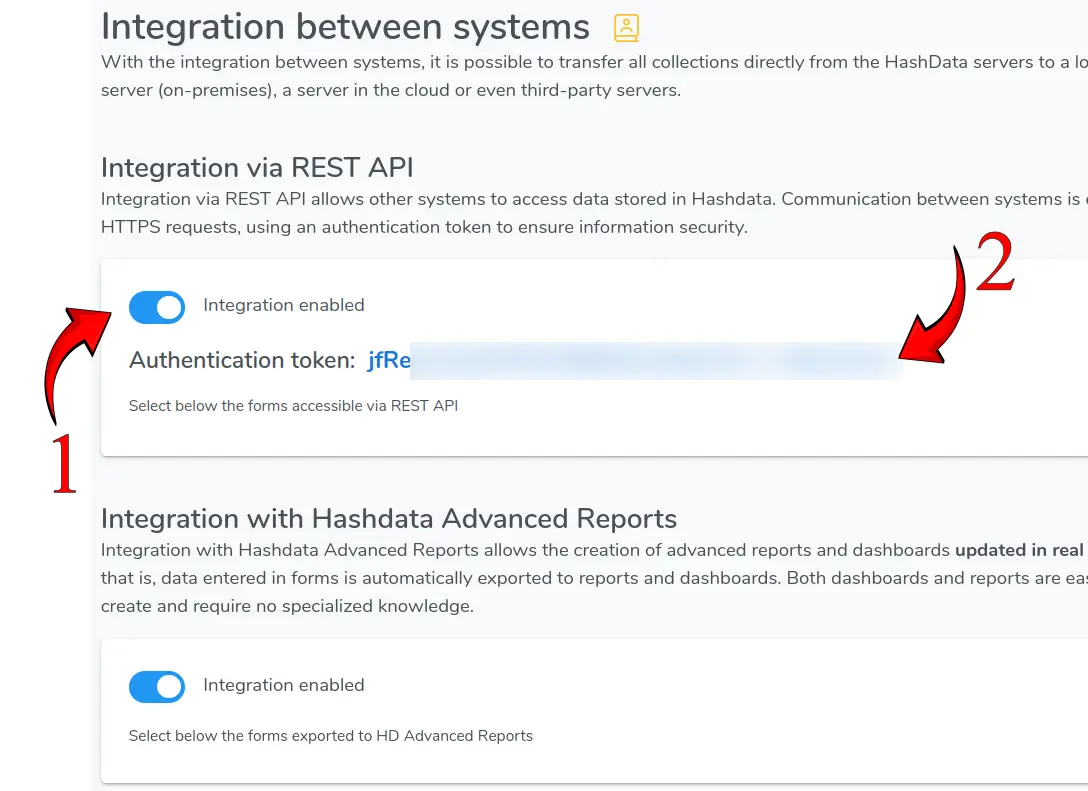
Authentication token, shown when enabling integration via REST API. Click on the image to enlarge it.
Sending the Authentication Token: URI vs. Header
In the Hashdata API, the authentication token can be sent in two ways to validate and authorize access to protected resources:
- Sending by URI (Query Parameter)
- Sending via HTTP Header (HD-API-TOKEN) 👈 RECOMMENDED option
Each method has advantages and disadvantages, especially when it comes to information security.
1. Sending the Token via URI
Example of a request with the token in the query string of the URL:
GET /users/export?token=abc123
Advantages
- ✅ Ease of implementation: it is simple to include the token as a parameter in the URL, without the need to modify request headers.
- ✅ Use in deep links: This can be useful when the client needs to share an authenticated link to a specific resource.
Disadvantages
- ❌ Exposure in logs and history: Since the URL is visible in the browser, user history, and server logs, the token can be easily compromised.
- ❌ Ease of interception: If the request is not protected by HTTPS, an attacker can capture the token by monitoring network traffic.
- ❌ Cache risk: Some proxy configurations and servers may store the URL with the token, allowing unauthorized access later.
2. Sending the Token via HTTP Header (HD-API-TOKEN)
Example of a request sending the token in the HTTP header:
GET /users/export
HD-API-TOKEN: abc123
Advantages
- ✅ Greater security: the token is not exposed in the URL, reducing the risk of leaks in logs, browsing histories or caches.
- ✅ Better access control: HTTP headers are easier to manipulate for security policies like CORS restrictions and protection against replay attacks.
- ✅ Supports JWT and OAuth authentication: This method is widely used for token-based authentication such as JWT (JSON Web Token) and OAuth 2.0.
Disadvantages
- ❌ Greater complexity in implementation: requires the client to correctly configure the request header, which can be more difficult in some applications.
- ❌ Incompatibility with some services: Certain browsers or HTTP clients may have restrictions on modifying custom headers.
All examples below assume that the authentication token will be sent via HTTP Header: HD-API-TOKEN
FORMS
To list the forms enabled for integration, use the following end-point:
GET https://api2.hashdata.app/v1/export/forms
Considering that in the example account the only form configured for integration is the "Personal Data Form", when executing the request to the forms end-point, a response is obtained as in the following example:
[
{
"form_id":"66f172c1dbb522a3729ab9a1",
"form_name":"Personal Data Form",
"form_status":"DRAFT"
}
]
Exported Attributes
You can create custom attributes (Exported Attributes) that can be used to select, filter, or group your forms and collections.
For example: Imagine that in an Organization there are some audit forms among hundreds of other forms and that the company wants to identify and export only the data from such forms without linking directly to the form ID. There are several ways to do this, one of which is to create an "Exported Attribute" called "form-type" with the value "audit" in all audit forms. Therefore, when exporting the list of forms, you can choose only the forms that have the value "audit" in the "form-type" key/field, e.g.:
[
{
"form_id":"66f172c1dbb522a3729ab9a1",
"form_name":"Personal Data Form",
"form_status":"DRAFT",
"form-type": "audit"
}
]
ANSWERS
To obtain the responses from a given form, you must enter the formId (form identifier):
GET https://api2.hashdata.app/v1/export/forms/{formId}/responses
The end-point also has the following optional parameters:
from/lastExecTime: DateTime - Starting date/time used to filter responses (JavaScrip Date or ISO 8601 UTC or epoch time);to/thisExecTime: DateTime - End date/time used to filter responses (JavaScrip Date or ISO 8601 UTC or epoch time);removeNewLineFromTexts: boolean - removes line breaks from text-type responses (recommended to set to 'true');<nome-do-campo>: text or number - filters by "field-name". View Field name in Element Attributes and Filter by form fields
Use the from and to parameters to paginate the response or to get the data progressively (as entered into the system).
The from and to parameters accept any JavaScript Date format, for example, a date in string format (ISO 8601): 2024-12-31T23:59:59.999Z (UTC time). Milliseconds are optional, e.g.: 2024-12-31T23:59:59Z
Examples:
- "2025-10-14"
- "2025-10-14T13:45:30"
- "2025-10-14T13:45:30.123Z"
- "2025-10-14T13:45:30+02:00"
- 1767225599000 (epoch time of "2025-12-31T23:59:59Z")
For example, the URI to access the responses of the "Personal Data Form" starting from 18:00:00 on December 31, 2025, in the official Brazilian time zone (zone offset -03:00) would be:
GET https://api2.hashdata.app/v1/export/forms/66f172c1dbb522a3729ab9a1/responses?from=2025-12-31T21:00:00Z
And, the URI to access the responses sent between 01/01/2025 and 02/01/2025 in Brazilian official time would be:
GET https://api2.hashdata.app/v1/export/forms/66f172c1dbb522a3729ab9a1/responses?from=2025-01-01T03:00:00Z&to=2025-01-02T03:00:00Z
Example HTTP call response (body)
[
{
"col_id": "6705960061539e305ab18576",
"form_id": "66f172c1dbb522a3729ab9a1",
"user_id": "64282604d86b5ebe18373ab2",
"collection_date": "2024-01-01T20:25:19.592Z",
"collection_received_date": "2024-01-01T20:30:01.156Z",
"auditor": "João da Silva",
"date": "2024-10-09T12:00:00",
"factory": "ABC",
"weight1": 22,
"weight2": 23,
"weight3": 21,
"calculated-average-weight": 22,
"audit-points": 706,
"audit-final-result": 95,
"form-type": "audit",
"nonconformities_files": ["6705960061539e734ea934ac", "6705960061539e734ea836ef"]
},
{ ... },
{ ... },
]
Filter by form fields (form questions)
We can use the questions from the forms in the filters, for example: in the case of the response/collection (JSON) shown above, we can filter all collections from the factory whose identifier is "ABC", e.g.:
GET https://api2.hashdata.app/v1/export/forms/66f172c1dbb522a3729ab9a1/responses?from=2025-01-01T15:00:00Z&fabrica=ABC
It is highly recommended to use the from and to parameters, or at least the from parameter, to limit the time frame where collections will be searched.
This way you will have a fast response, with low latency.
If you do not specify any of the mentioned parameters, the system will search all collections and this may take a while, resulting in high latency.
DOWNLOAD IMAGES AND OTHER FILES
Various types of files can be attached to form questions, such as photos, spreadsheets, documents, etc. To search for any file attached to a response, use the end-point:
GET https://api2.hashdata.app/v1/export/forms/{{formId}}/responses/{{responseId}}/files/{{fileId}}
In the above URL, replace the parameters {{formId}}, {{responseId}}, and {{fileId}} with the data obtained from the collection.
In the case of the collection mentioned above, used as an example, the values would be:
formId: 66f172c1dbb522a3729ab9a1 ➡️form_idresponseId: 6705960061539e305ab18576 ➡️col_idfileId: 6705960061539e734ea934ac ➡️non-conformities_files
CONTRIBUTORS (USERS)
To list all collaborators in a given workspace, use the following endpoint:
GET https://api2.hashdata.app/v1/export/users
By default, this end-point returns data in JSON format. When executing the request without providing parameters, you get a response like the one in the following example:
[
{
"user_id":"66ae9f205c7ed7e95d183804",
"user_nickname":"Pedro",
"user_full_name":"Pedro Alcântara",
"user_department":""
},
{
"user_id":"6752ff2b2536410b2897de91",
"user_nickname":"José",
"user_full_name":"José da Silva",
"user_department":""
}
]
It is possible to receive employee data in CSV (Comma-Separated Values) format. To do this, simply provide two more
parameters: format and separator. For example:
GET https://api2.hashdata.app/v1/export/users?format=csv&separator=;
Obtaining the following result:
user_id;user_nickname;user_full_name;user_department
66ae9f205c7ed7e95d183804;Pedro;Pedro Alcântara;
6752ff2b2536410b2897de91;Jose;Jose da Silva;